Underground Storage Well
Risk Assessment
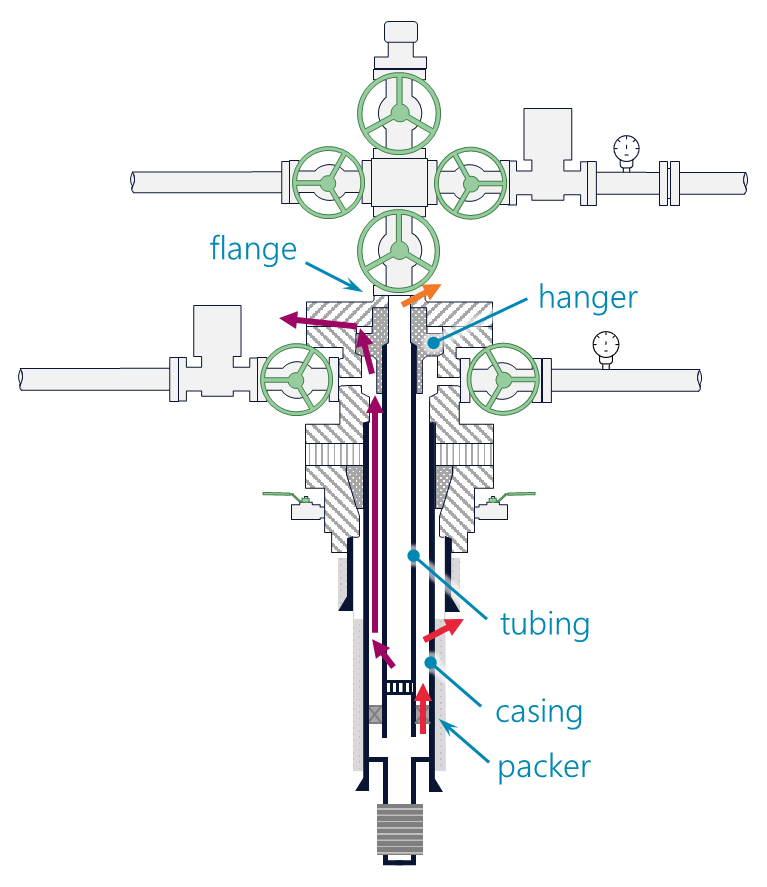
Integral Engineering has developed a fully quantitative framework for risk assessment of natural gas storage wells, including the wellhead and connected piping. The framework uses a dynamic fault tree to estimate the probability of an accidental release to the atmosphere and the resulting hazards. The modular architecture of the framework allows operators to use threat‑specific models with differing levels of sophistication which minimizes the overall complexity of the analysis.
The potential for barrier failure is assessed for over 80 potential failure mechanisms, including:
internal and external corrosion
erosion
component failures, with models for wellhead flanges, valves, casing and tubing connections, and packers
casing wear
external interference from vehicle impacts, vandalism, excavations, lifting operations, and aircraft crashes
The framework reflects the interplay between the various barriers to failure in a well and the effect that wellhead spacing, cement quality, and well-inflow performance have on the expected consequences. The life safety risk for an ignited natural gas release is assessed by calculating the release rate, the hazard area from the resulting jet fire model, and the thermal radiation dosage to people or equipment within the area.
By calculating the rates of failure and the associated consequences, you can quantify the benefits of integrity management activities such as wireline inspections, continuous pressure monitoring, erosion monitoring programs, and adding protections to minimize risk from vehicle collisions. The approach has been developed to meet and exceed the risk assessment requirements of API RP 1170 and API RP 1171 (incorporated by reference in U.S. regulation 49 CFR 192.12) and the recent changes to the California Code of Regulations.
Contact us to find out how more about how we can help you implement storage risk assessment.
Our Publications
IPC2022-86833
A Quantitative Risk Assessment Framework for Natural Gas Storage Wells
A quantitative framework for risk assessment of natural gas storage wells, including the wellhead and connected piping, has been developed to assess SoCalGas’s underground gas storage sites in California. The approach has been developed to meet and exceed the risk assessment requirements of API RP 1171 and the recent changes to the California Code of Regulations. Further, several of the recommendations made in the recent PHMSA study, “Risk Assessment and Treatment of Wells” (2021), have been addressed and incorporated. …
IPC2022-86734
Modelling Accidental Impact Threats to Natural Gas Storage Wells
A quantitative risk assessment framework has been developed for SoCalGas’s underground gas storage sites in California. This framework includes quantitative models for accidental impact threats to the wellhead and lateral piping, including damage from excavations, vehicle collisions, lifting operations, and aircraft crashes (for first, second, and third parties). In an industry survey of underground storage operators conducted by the Gas Research Institute in 2004, 15% of the recorded significant release incidents were due to accidental impact threats. …
IPC2022-86794
Probabilistic Corrosion Assessment for Natural Gas Storage Wells
As a well ages, metal loss on the casing can grow, increasing the probability of a failure from corrosion. Inspection and repair programs manage this probability by reducing uncertainty in the casing condition and repairing significant metal loss anomalies. However, performing a casing inspection involves a considerable amount of risk, which can vary depending on the well configuration. The benefit of inspection and repair needs to be balanced with the inspection risk to determine the interval that minimizes the overall risk. …